SECTION – IV
Mathematics (गणित)
Q91. The digit form of one crore one lac one thousand one hundred and one, is
(A) 11111101
(B) 10101101
(C) 10010101
(D) 11101001
एक करोड़ एक लाख एक हजार एक सौ एक का अंकीय रूप है
(A) 11111101
(B) 10101101
(C) 10010101
(D) 11101001
Answer – B
Q92. If 31P5 is multiple of 3. where P is ten’s digit, then the greatest value of P is
(A) 9
(B) 3
(C) 6
(D) 5
यदि 31P5, 3 का गुणज है, जहाँ P दहाई का अंक है, तो P का अधिकतम मान है
(A) 9
(B) 3
(C) 6
(D) 5
Answer – A
Q93. Value of 25+12×33-25÷5 is
(A) 1216
(B) 79 ⅕
(C) 416
(D) 239 ⅕
25+12×33-25÷5 का मान है
(A) 1216
(B) 79 ⅕
(C) 416
(D) 239 ⅕
Answer – C
Q94. The least number which is divisible by the numbers 1 to 10 is
(A) 1680
(B) 840
(C) 2520
(D) 5040
वह कौन-सी छोटी से छोटी संख्या है जो 1 से 10 तक की संख्याओं से विभाज्य है ?
(A) 1680
(B) 840
(C) 2520
(D) 5040
Answer – C
Q95. Multiplication of place values of 3, 4 and 5 in the number 60321045 is equal to
(A) 60
(B) 600000
(C) 60000
(D) 60000000
संख्या 60321045 में 3, 4 तथा 5 के स्थानीय मानों का गुणनफल बराबर है
(A) 60
(B) 600000
(C) 60000
(D) 60000000
Answer – D
Q96. The non-terminating recurring number 0:123 is equal to the fraction,
(A) 123/1000
(B) 41/333
(C) 37/300
(D) 41/330
अनवसानी आवर्ती संख्या 0-123 के बराबर भिन्न है
(A) 123/1000
(B) 41/333
(C) 37/300
(D) 41/330
Answer – C
Q97. The cost of 16 coins of 50 paise is equal to
(A) 4 coins of Re. 1 + 3 coins of Rs. 2
(B) 3 coins of Rs. 2 + 8 coins of 25 paise
(C) 3 coins of Rs. 2 + 6 coins of 25 paise
(D) 2 coins of Rs. 2 + 3 coins of Re. 1
50 पैसे के 16 सिक्कों का मूल्य बराबर है
(A) 1 रुपये के 4 सिक्के + 2 रुपये के 3 सिक्के
(B) 2 रुपये के 3 सिक्के + 25 पैसे के 8 सिक्के
(C) 2 रुपये के 3 सिक्के + 25 पैसे के 6 सिक्के
(D) 2 रुपये के 2 सिक्के + 1 रुपये के 3 सिक्के
Answer – B

Answer – A
Q99.
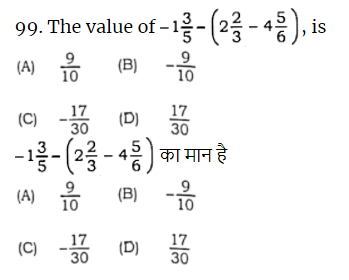
Answer – D
Q100. The greatest number which divides 244 and 2052 such that it leaves remaining 4 in each case, is
(A) 12
(B) 16
(C) 30720
(D) 15360
बड़ी से बड़ी संख्या, जिससे 244 तथा 2052 को विभाजित करने पर पर प्रत्येक स्थिति में 4 शेष प्राप्त हो, वह संख्या है
(A) 12
(B) 16
(C) 30720
(D) 15360
Answer – B
Q101. The difference between the greatest and the lowest prime number digits is
(A) 88
(B) 86
(C) 89
(D) 95
दो अंकों की सबसे बड़ी व सबसे छोटी अभाज्य संख्या में अन्तर है
(A) 88
(B) 86
(C) 89
(D) 95
Answer – B
Q102. If the cost of 12 dozen pens is Rs. 720, then the cost of 25 pens is
(A) Rs. 1,500
(B) Rs. 150
(C) Rs. 125
(D) Rs. 1,250
यदि 12 दर्जन पेनों का मूल्य 720 रुपये है. तो 25 पेनों का मूल्य होगा
(A) 1,500 रु०
(B) 150 रु०
(C) 125 रु०
(D) 1,250 रु०
Answer – C
Q103. Average weight of 5 students is 40 kg. If one student of weight 50 kg has left them, then the average weight of remaining students is
(A) 50 kg
(B) 37.5 kg
(C) 30 kg
(D) 62.5 kg
5 छात्रों का औसत भार 40 किग्रा है। यदि उनमें से एक छात्र जिसका भार 50 किग्रा है, छोड़ जाता है, तो शेष बचे छात्रों का औसत भार होगा
(A) 50 kg
(B) 37.5 kg
(C) 30 kg
(D) 62.5 kg
Answer – B
Q104. If a product is sold on 10% profit at selling price Rs. 330, then cost price of the product is
(A) Rs. 360
(C) Rs. 297
(B) Rs. 363
(D) Rs. 300
एक वस्तु 10% लाभ से विक्रय मूल्य 330 रु. पर बेची जाती है, तो उस वस्तु का क्रय मूल्य है
(A) 360 रु०
(B) 363 रु०
(C) 297 रु०
(D) 300 रु०
Answer – D
Q105. In a school under ‘shramdan’ camp, 12 students clean for 7 hours. If equal part needs to be cleaned in 6 hours, then how many students will be required ?
(A) 14
(B) 12
(C) 16
(D) 15
एक विद्यालय में ‘श्रमदान’ शिविर के अन्तर्गत 12 छात्र, 7 घण्टे सफाई कर 6 घण्टे में साफ करना हो, तो कितने छात्रों की आवश्यकता होगी।
(A) 14
(C) 16
(B) 12
(D) 15
Answer – A
Q106. P takes loan of Rs. 9,000 at the rate of simple interest 8.5% for 2 years and 8 months, then total amount to be returned by him will be
(A) Rs. 2,040
(B) Rs. 3,060
(C) Rs. 11,040
(D) Rs. 12,060
P ने 9,000 रु० का ऋण 8.5% साधारण ब्याज दर पर 2 वर्ष 8 माह के लिए लिया, तो उसे कुल कितनी राशि पुनः लौटानी पड़ेगी ?
(A) 2,040 रु०
(B) 3.060 रु०
(D) 11,000 रु०
(D) 12,060 रु०
Answer – C
Q107. A cylinder of height cm is formed after folding ( without overlapping ) a 22 cm × 4 cm rectangular paper, then curved surface area of this cylinder, is
(A) 88 π cm2
(B) 88 cm2
(C) 176 π cm2
(D) 176 cm2
एक 22 सेमी × 4 सेमी के आयताकार कागज को मोड़ कर (बिना अधिव्यापन), एक 4 सेमी ऊँचाई का बेलन बनाया गया। इस बेलन का वक्रपृष्ठ का क्षेत्रफल होगा
(A) 88 π cm2
(B) 88 cm2
(C) 176 π cm2
(D) 176 cm2
Answer – B
Q108. In the given figure lines AB and CD are intersecting at point O. If OE and OF are angle bisectors of ∠BOD and ∠COB respectively, and if ∠EOD=25° then ∠COF is equal to
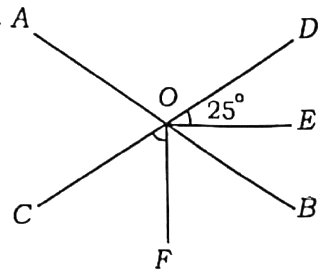
(A) 130°
(B) 65°
(C) 105°
(D) 50°
दिये गये चित्र में रेखाएँ AB तथा CD, बिन्दु O पर प्रतिच्छेद करती हैं। यदि OE तथा OF क्रमशः ∠BOD तथा ∠COB के समद्विभाजक है एवं यदि ∠EOD = 25°, तो ∠COF बराबर है

(A) 130°
(B) 65°
(C) 105°
(D) 50°
Answer – B
Q109. Area of a square field is 6400 m2. The distance travelled by a person, in 5 rounds on its perimeter, is
(A) 320 m
(B) 160 m
(C) 1.6 km
(D) 3.2 km
एक वर्गाकार मैदान का क्षेत्रफल 6400 वर्ग मी है। एक व्यक्ति द्वारा इस मैदान की परिमित पर 5 चक्कर लगाने पर तय दूरी होगी
(A) 320 m
(B) 160 m
(C) 1.6 km
(D) 3.2 km
Answer – C
Q110. Time taken to fill a water tank of size 2 m × 1.5 m × 1 m, by a tap with speed 20 litre/minute, is
(A) 9 minutes
(B) 1 hour 30 minutes
(C) 60 minutes
(D) 2 hours 30 minutes
2 m × 1.5 m × 1 m नाप के पानी के टैंक को एक नल द्वारा 20 लीटर/मिनट की गति से भरने में लगा समय है
(A) 9 मिनट
(B) 1 घण्टा 30 मिनट
(C) 60 मिनट
(D) 2 घण्टे 30 मिनट
Answer – D
Q111. How many bricks of measure 25 cm × 16 cm × 10 cm are required to make a wall of size 20 m long, 5 m high, 50 cm thick, while there are two doors of size 2 m × 1.5 m in the wall ?
(A) 11750
(B) 11000
(C) 117500
(D) 97500
20 मीटर लम्बी, 5 मीटर ऊँची और 50 सेमी मोटी दीवार जिसमें दो दरवाजे 2 मीटर × 1.5 मीटर माप के हैं, बनाने में 25 सेमी × 16 सेमी × 10 सेमी माप की कितनी ईंटों की आवश्यकता होगी ?
(A) 11750
(B) 11000
(C) 117500
(D) 97500
Answer – A
Q112. In given figure OP||RS, ∠OPQ = 100° and ∠QRS = 140°, then ∠PQR is equal to
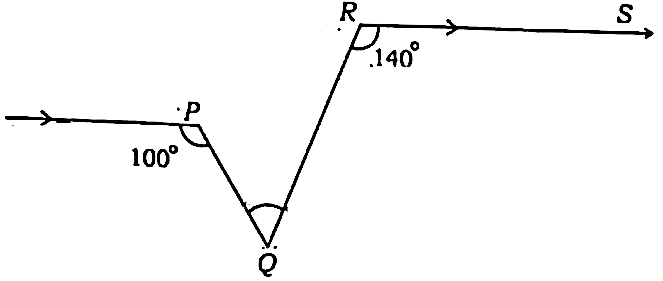
(A) 80°
(B) 60°
(C) 70°
(D) 50°
दिए गए चित्र में OP||RS, ∠OPQ = 100° तथा ∠QRS = 140° तो ∠PQR बराबर होगा

(A) 80°
(B) 60°
(C) 70°
(D) 50°
Answer – B
Q113. For multiplication of two decimal numbers, such as 0.4 × 0.2 = 0.08, an appropriate teaching-learning tool to explain the concept is
(A) Dienes block
(B) Number chart
(C) Counting star (abacus)
(D) Graph paper
दो दशमलव संख्याओं का गुणन जैसे 0.4 × 0.2 = 0.08 की संकल्पना का शिक्षण-अधिगम साधन है
(A) डायनिस ब्लॉक
(B) संख्या चार्ट
(C) गिनतारा (अबेकस)
(D) ग्राफ पेपर
Answer – D
Q114. Which of the following represents 9, using tally marks?
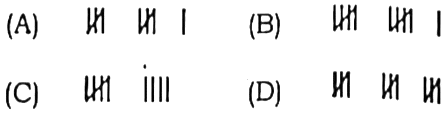
मिलान चिह्नों का उपयोग करते हुए निम्नलिखित में से कौन संख्या 9 को प्रदर्शित करेगी ?
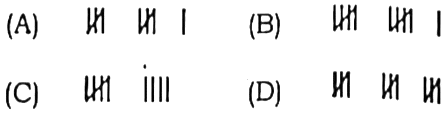
Answer – C
Q115. If monthly salary of a person is Rs. 24,000, central angle of the sector, showing the expenditure on education by pic-chart is 60°, then the expenditure on education is
(A) Rs. 4,000
(B) Rs. 8,000
(C) Rs. 3,000
(D) Rs. 6,000
एक व्यक्ति का मासिक वेतन 24,000 रु० है। उसके शिक्षा पर किये व्यय को पाई-चार्ट पर दर्शाने वाले त्रिज्यखण्ड का केन्द्रीय कोण 60° है, तो उसका शिक्षा पर व्यय होगा
(A) 4,000 रु०
(B) 8,000 रु०
(C) 3,000 रु०
(D) 6,000 रु०
Answer – A
Q116. “Mathematics is the mirror of civilization and culture.” This statement is said by
(A) Bacon
(B) Berthelot
(C) Hogben
(D) Bertrand Russel
“गणित सभ्यता और संस्कृति का दर्पण है।” यह कथन किसने कहा ?
(A) बेकन
(B) बर्थलॉट
(C) हॉगबेन
(D) बर्टेण्ड रसैल
Answer – C
Q117. “The act of combining separate parts.” This method is called
(A) Analytic Method
(B) Synthetic Method
(C) Laboratory Method
(D) Project Method
“अलग-अलग भागों को जोड़ना।” यह सिद्धान्त कहलाता है
(A) विश्लेषण विधि
(B) संश्लेषण विधि
(C) प्रयोगशाला विधि
(D) परियोजना विधि
Answer – B
Q118. The maximum success of remedial teaching depends
(A) time and duration
(B) the correct identification of causes of problem
(C) knowledge of linguistic rules
(D) remedial teaching materials
उपचारात्मक शिक्षण की सर्वाधिक सफलता निर्भर करती है –
(A) समय व अवधि पर
(B) समस्या के कारणों की सही पहचान पर
(C) भाषाई नियमों के ज्ञान पर
(D) उपचारात्मक शिक्षण सामग्री पर
Answer – B
Q119. Arrange in correct order the steps of evaluation in mathematics :
- Identification of situations
- Selection of objectives
- Selection of evaluation methods
- Interpretations of evidences
- Constructions of evaluation devices
(A) 2, 1, 3, 5, 4
(B) 2, 3, 1, 5, 4
(C) 2, 3, 5, 4, 1
(D) 3, 2, 4, 5, 1
गणित में मूल्यांकन के सोपानों का सही क्रम बताएं : - परिस्थितियों की पहचान
- उद्देश्यों का चयन
- मूल्यांकन विधियों का चयन
- प्रमाणों की व्याख्या
- मूल्यांकन प्रविधियों का निर्माण
(A) 2, 1, 3, 5, 4
(B) 2, 3, 1, 5, 4
(C) 2, 3, 5, 4, 1
(D) 3, 2, 4, 5, 1
Answer – A
Q120. A student was asked to read the following numbers :
306, 406, 408, 4020
He reads as follows:
Thirty six, forty six, forty eight, forty twenty
The reason for error in reading is that
(A) the student does not like maths class and finds the class boring
(B) the student has understood the concept of place value and its use also
(C) the student is not fit for study of maths
(D) the student is not able to understand the concept of place value and feels comfortable using two-digit numbers only
किसी छात्र से नीचे दी गई संख्याओं को पढ़ने के लिए कहा गया :
306, 406, 408, 4020
उसने इन्हें इस प्रकार पढ़ा :
तीस छः, चालीस छः, चालीस आठ, चालीस बीस
पढ़ने में त्रुटि का कारण है कि
(A) छात्र को गणित की कक्षा अच्छी नहीं लगती और कक्षा उबाऊ लगती है
(B) छात्र ने स्थानीय मान की संकल्पना को समझ लिया है तथा उसका उपयोग भी
(C) छात्र गणित का अध्ययन करने के लिए उपयुक्त नहीं है
(D) छात्र स्थानीय मान की संकल्पना को नहीं समझता है और उसे केवल दो-अंकीय संख्याओं को पढ़ना आसान लगता है।
Answer – D